Iran’s Vital Oil Industry Is Vulnerable in an Escalating Conflict


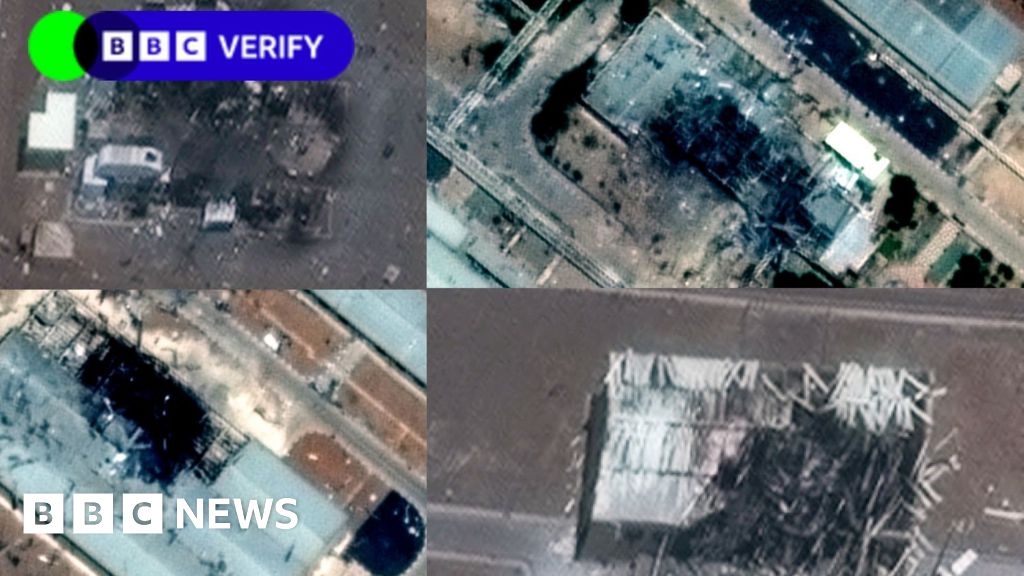
The country’s exports mostly come from Kharg Island in the Persian Gulf. But Israel’s energy facilities are also at risk. The conflict between Israel and Iran appeared to be spreading on Saturday to Iran’s energy infrastructure, raising fears about energy supplies from the Middle East. Iran’s oil ministry blamed Israeli drones for attacking part of the South Pars natural gas field, one of the world’s largest, and a refinery, causing fires at both. It is not clear how far Israel intends to go in attacking Iran’s energy facilities, a crucial source of export cash for the country as well as domestic energy that looks particularly vulnerable. “This is a first salvo into energy and a warning shot that Israel is willing to hit Iranian energy infrastructure if Israeli civilians are targeted,” said Richard Bronze, head of geopolitics at Energy Aspects, a research firm. Other Iranian installations are at risk, analysts say. “There is one clear target that would make it very easy if Israel or the United States wanted to impact Iran’s oil exports,” Homayoun Falakshahi, senior analyst for crude oil at Kpler, a research firm, said during a webinar on Friday. “And this is Kharg Island.” Nearly all of Iran’s oil exports leave from tankers at berths around Kharg Island, a small coral land mass in the northern part of the Persian Gulf off the Iranian coast, potentially making it a target in a protracted war, analysts say. Iran has been developing another terminal in Jask, a coastal city just outside the Strait of Hormuz on the Gulf of Oman, but its capacity appears to be limited, Mr. Falakshahi said. Israel’s energy system also looks exposed, analysts say, which could potentially restrain its attacks. Were the fighting to escalate to major energy installations across the region, the consequences could be serious not only for Iran and its neighbors but for their customers, especially in Asia, and world markets. Oil prices have already jumped since the Israeli attack early Friday. Any escalation that might appear to threaten international supplies could send prices soaring. Iran’s coastline stretches along the northern shore of the Strait of Hormuz, a narrow passageway through which tankers and other ships must pass on their way from the Persian Gulf to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean. Iran has a history of interfering with shipping in the area. Kpler has estimated that 21 percent of the world’s liquefied natural gas, most of it from Qatar, flowed through this gauntlet in 2024. A hefty 14 million barrels of crude oil a day also moves through the strait, according to Kpler’s estimates. The conflict with Israel comes at a delicate point for Iran’s petroleum industry, which is a crucial pillar for its economy and its ability to fund its nuclear program. Strikes on the Iranian facilities could potentially negate years of effort to rebuild production from the low levels at the beginning of this decade when President Trump pulled out of a deal reached by President Barack Obama under which Iran agreed to curbs on its nuclear program in return for an easing of sanctions, including on its oil sales. Oil production in Iran has increased around 75 percent to about 3.4 million barrels a day from depressed 2020 levels, while exports have roughly tripled, according to estimates from the International Energy Agency and Kpler. FGE, an energy consulting firm, estimates that Iranian energy export revenues, including oil products and electricity, have almost quadrupled since 2020 to $78 billion in 2024. Even before the Israeli strikes, Iran faced major handicaps. Although it has some of the world’s richest troves of oil and natural gas, it has strained to exploit them largely because of protracted political tensions with the West dating to the establishment of the Islamic Republic in 1979. These frictions have kept Western firms from working in Iran for years. Lack of capital and expertise has limited development of oil and natural gas fields and access to major investment projects like liquefied natural gas facilities that might have benefited the Iranian industry. Qatar, whose huge gas fields in the Persian Gulf border Iran’s, has become rich through L.N.G. development with western partners like Shell and Exxon Mobil, which allow the natural gas to be exported to Europe and Asia. Despite having large natural gas resources, Iran has recently struggled to produce enough fuel to prevent power cuts. Much of Iran’s petroleum infrastructure, including the refineries that supply products like gasoline to local markets, are old. If these facilities suffered significant damage, Iran “might struggle more than maybe other countries” to find the spare parts and international support to repair them, Mr. Bronze said. Sanctions also mean that few customers are willing to buy Iranian oil. Nearly all of Iran’s crude exports go to China. The main buyers are small refiners there, known as “teapots” Mr. Falakshahi said, that are able to extract a substantial discount of up to $7 a barrel from the Iranians. If those refiners were unable to buy Iranian crude, they would need to look elsewhere, potentially tightening global markets. Even before the current conflict, signs were emerging of pressure on Iranian oil exports. The Trump administration has been tightening sanctions that saw a de facto easing in the Biden administration. Chinese imports dropped substantially in May, according to Kpler’s estimates. Analysts say Israel’s energy infrastructure could also prove vulnerable. Already, the Israeli government has as a precaution ordered a production halt at two of the country’s three offshore natural gas platforms, including Leviathan, which is operated by Chevron. Gas fuels most of Israel’s electric power generation. If this stoppage continued, it could also reduce or halt gas exports to Egypt, hurting customers there. Israel is also heavily dependent on imported oil brought through the port of Ashkelon in the south of the country. “They are also very fragile,” Mr. Falakshahi said of Israel. The Saudis and the United Arab Emirates have worked in recent years to ease tensions with Iran and head off future incidents like the attack on a Saudi Aramco facility called Abqaiq in 2018 that temporarily knocked out about half of the kingdom’s export capacity. Those attacks were claimed by the Houthi militant group in Yemen, but the United States at the time blamed Iran for them. Analysts have said it is conceivable that if Iran feels sufficiently threatened, it could target petroleum installations in those countries again. “The question is,” Mr. Bronze said, how would Iran respond “if it feels like its core economic interests, its energy system, have been attacked.” Farnaz Fassihi contributed reporting.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0